- What is Agile?
- When to use Agile?
- Traditional approaches
- Agile Characteristics
- Test Driven Development in Agile
- Agile Manifesto
What is Agile?
- There are several different definitions of agile.
- The Agile Alliance (2021) defines agile as “the ability to create and respond to change.”
- Merriam-Webster dictionary (2021) defines agile as “marked by ready ability to move with quick easy grace,” like an agile dancer.
- PMI’s Agile Practice Guide (2017) defines agile as “a term used to describe a mindset of values and principles as set forth in the Agile Manifesto.”
- Agile is simply a concept that states how work should be done.
- This work can be a part of a project or regular operations.
- The concept of Agile has several different implementations, which are called methodologies.
- These methodologies can either be applied individually to work or together in combination.
- Most common Agile implementations are a combination of several Agile methodologies.
When to use Agile?
- Agile is not recommended for all kind of work.
- There are two pre-requisites that need to be satisfied to get the real benefits of Agile.
- These pre-requisites are:
- Work has high uncertainty/flexibility in scope
- Work involves “knowledge workers” – The term “knowledge workers” stands for highly skilled resources. One of the key characteristics of Agile is to give a lot of decision-making authority to the team. Hence, the team needs to have the required skills to take proper decisions.
Traditional approaches
Characteristics of traditional approaches
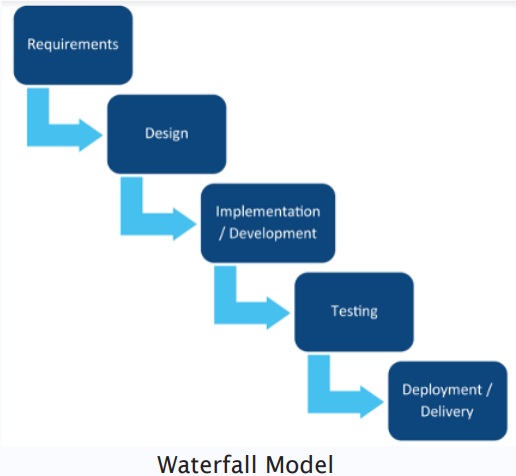
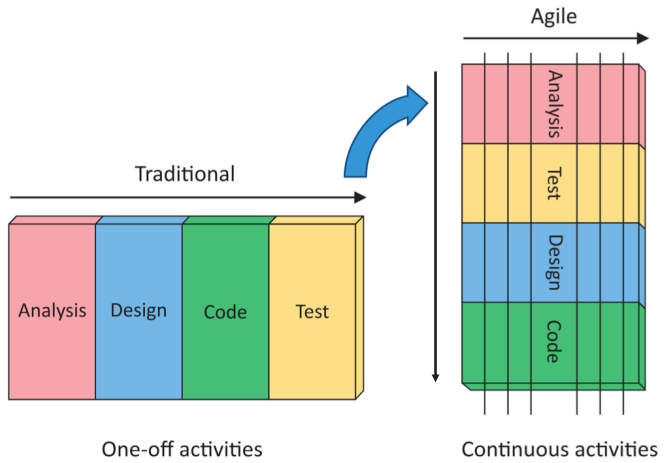
- The traditional approach to perform work was to gather and document all the requirements in the beginning, plan all of them at once, and then begin execution.
- Customer gets to see the final deliverables only when almost all the stages are complected.
- This approach is sometimes even referred to as the “Big Bang Approach”, as all the deliverables are shown to the customer together at a later part of the project.
Issues with the Traditional Approaches
- If at the final stage the customer does not like some of the deliverables and requests major changes, then one needs to go back to the previous stages of requirements, design, or development to incorporate them.
- This could involve a lot of rework, which involves time, effort, and money. Hence, making changes using this approach was quite cumbersome.
- Customer needs to request for changes anywhere during the stages, for example, during development or testing, then once again that could involve a lot of rework by going back to the previous stages.
- Handling changes could be quite a challenge in the sequential model.
- Due to this, the team is most often reluctant to incorporate changes in the work.
- This means that the team is not customer centric (does not concentrate on the customer’s benefit).
Agile Characteristics
Incremental
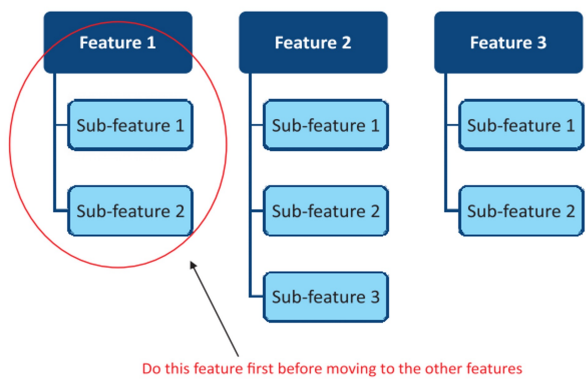
The entire system is divided into pieces and built piece by piece.
For example, if we have requirements for building various features of a system, and each feature is divided into sub-features, we will build all sub-features of one feature before moving to the next feature.
Iterative
- A few initial parts of the system are built and improved upon as we get customer feedback.
- The entire system is built little by little and continuously improved until it is acceptable.
- For example, if we have requirements for building various features of a system, and each feature is divided into sub-features, we will build a few sub-features of multiple features before moving to the rest of the sub-features.
Adaptive
- Being able to change course rapidly and easily is one of the key characteristics and the foundation of Agile.
Test Driven Development in Agile
- Test is coming in an earlier stage in Agile. This is not a mistake but by design. This is based on a concept called Test Driven Development (TDD), that is commonly practiced in Agile.
Test-Driven Development (TDD): This is an approach where developers write tests before they write the actual code. They first write a test that fails (because the functionality doesn’t exist yet), then they write the code to make that test pass, and finally refactor the code to acceptable standards.
In Agile methodologies, early testing is crucial for the following reasons:
- Quality Delivery: Ensure each sprint produces a quality product increment.
- Continuous Feedback: Offer immediate feedback to developers, allowing for swift adjustments.
- User Story Validation: Confirm that user stories fulfill their acceptance criteria.
- Risk Management: Identify and address high-risk areas early in the process.
- Support for CI: Align with the principles of Continuous Integration.
- Built-in Quality: Focus on building quality from the start, rather than adding it later.
- Cost Efficiency: Detect and rectify defects early to save time and resources.
- Customer Satisfaction: Prioritize and ensure consistent value delivery to customers.
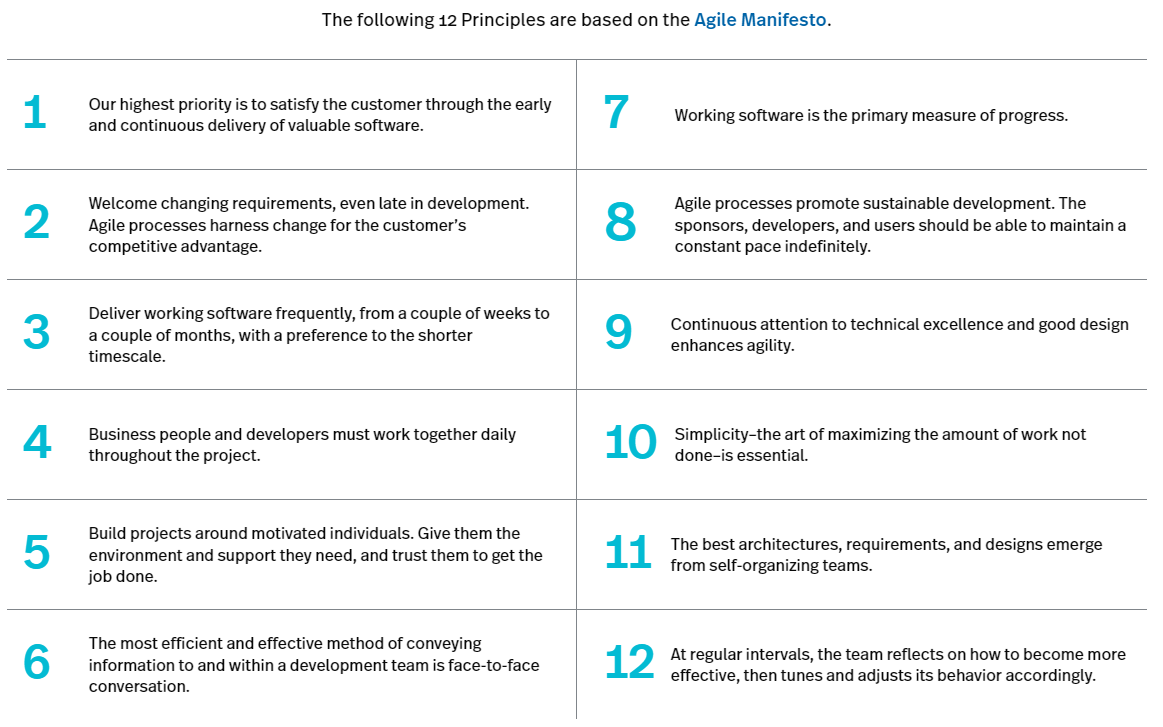
Agile Manifesto
The work we do in Agile must adhere to the Agile Manifesto:
Agile Manifesto Values
Agile Manifesto Principles
Agile Methodologies
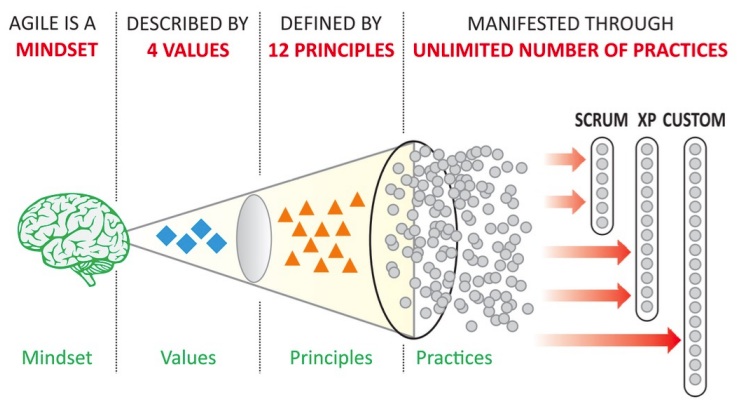
Values and Principles of Agile are implemented through several Practices. These practices are defined as part of several Agile Methodologies:
- Scrum
- XP (eXtreme Programming)
- Lean (aligned closely to Agile, but not really an Agile methodology)
- Kanban (implementation of Lean)
- FDD (Feature Driven Development)
- Crystal
- DSDM (Dynamic Systems Development Method)