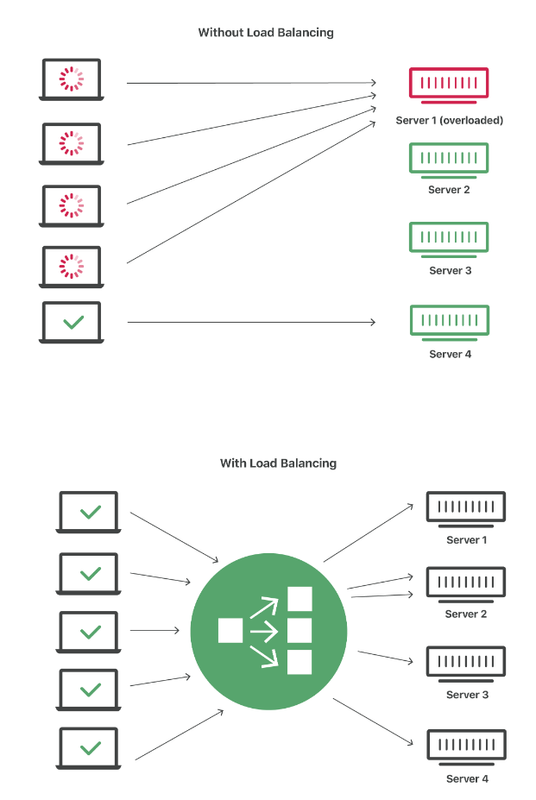
Single server, no matter how optimised, no matter how good hardware is used, there will always be a performance ceiling. When the performance of a single server cannot meet the business needs, it is necessary to design high-performance clusters (multiple servers) to improve the overall processing performance of the system.
Load balancing is a crucial technique in network and application infrastructure, ensuring that workloads are distributed evenly across multiple servers. This helps enhance performance, improve resource utilization, and ensure high availability and reliability.
- What is Load Balancing?
- Types of Load Balancing
- Load Balancing Architecture
- Load Balancing Algorithm (Methods)
What is Load Balancing?
Load balancing is the process of distributing incoming network traffic or workloads across multiple servers or resources to ensure no single server becomes overwhelmed. By spreading the load, it helps maintain system performance and availability, especially during high traffic periods.
Benefits of Load Balancing
- Improved Performance: Distributes workloads evenly to prevent server overload, ensuring faster response times.
- High Availability: Ensures that if one server fails, others can take over, minimizing downtime.
- Scalability: Makes it easier to add or remove servers as demand changes.
- Resource Optimization: Ensures efficient use of available resources, reducing the risk of underutilization or overutilization.
Types of Load Balancing
DNS Load Balancing
DNS load balancing uses the Domain Name System (DNS) to distribute traffic among multiple servers by rotating the IP addresses associated with a domain name. When a DNS request is made, the DNS server responds with different IP addresses in a round-robin fashion.
- How It Works
- Round-Robin DNS: The DNS server cycles through a list of IP addresses, responding with a different address each time a request is made.
- GeoDNS: Directs traffic based on the geographic location of the user, reducing latency and improving performance.
- Advantages
- Simple Setup: Easy to configure and implement.
- Geographic Distribution: Can reduce latency by directing users to the nearest server.
- Disadvantages
- No Real-Time Health Checks: Does not account for server health, potentially directing traffic to downed servers.
- Limited Load Balancing Logic: Basic round-robin distribution may not account for server load or capacity.
Hardware Load Balancing
Hardware load balancers are physical devices that sit between the client and backend servers, distributing incoming traffic based on various algorithms. These devices are designed to handle high traffic volumes and provide advanced load balancing features.
Popular hardware load balancers include F5 Networks BIG-IP, Cisco ACE, and Citrix NetScaler.
- How It Works
- Load Distribution Algorithms: Uses algorithms like round-robin, least connections, and IP hash to distribute traffic.
- Health Checks: Continuously monitors the health of backend servers to ensure traffic is only directed to available servers.
- SSL Offloading: Offloads SSL encryption and decryption tasks from backend servers, improving performance.
- Advantages
- High Performance: Capable of handling large volumes of traffic with minimal latency.
- Advanced Features: Offers advanced load balancing techniques, health checks, and security features.
- Disadvantages
- Cost: Expensive to purchase and maintain.
- Scalability: Limited by the capacity of the physical device.
Software Load Balancing
Software load balancers are applications or services that run on standard hardware or virtual machines. They provide flexible and scalable load balancing solutions, often integrated into cloud environments or modern application architectures.
Popular software load balancers include HAProxy, Nginx~~~~, and AWS Elastic Load Balancing (ELB).
- How It Works
- Software-Based Algorithms: Implements various load balancing algorithms such as round-robin, least connections, and IP hash.
- Health Checks: Monitors the health of backend servers and redirects traffic as needed.
- Integration: Can be integrated with container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes.
- Advantages
- Cost-Effective: Cheaper than hardware load balancers, as they run on existing hardware.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Easy to scale by deploying additional instances or adjusting configurations.
- Integration: Can be easily integrated into cloud environments and modern architectures.
- Disadvantages
- Performance Overhead: May introduce latency if not optimized properly. Not as powerful as hardware load balancing.
- Resource Intensive: Consumes CPU and memory resources on the host machine.
Load Balancing Architecture
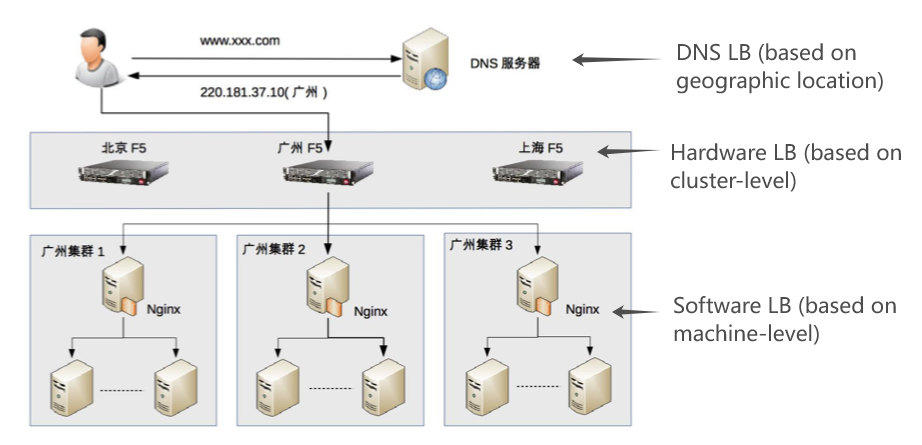
The three types of load balancing mentioned above all have some advantages and disadvantages, but it does not mean that in practice you can only make a single choice based on their advantages and disadvantages. Instead, you can use a combination of them based on their strengths and weaknesses.
Specifically, the basic principles of the combination are:
- DNS load balancing for geographic load balancing;
- Hardware load balancing for cluster-level load balancing;
- Software load balancing for machine-level load balancing.
For example, the following figure shows an example of the combination of 3 types of LBs. The load balancing of the whole system is divided into three layers:
Load Balancing Algorithm (Methods)
Load balancing algorithms are many and varied, and it is difficult to remember them all. But after extracting the commonalities, there are only these 4 categories:
- Round Robin (Weighted Round Robin)
- Lowest Load First
- Highest Performance First
- Hash
Round Robin
The Round Robin algorithm distributes incoming requests to a list of servers in a sequential, cyclic order. Each server receives an equal number of requests, ensuring a balanced load distribution.
- How It Works
- The load balancer maintains a list of servers.
- Each incoming request is forwarded to the next server in the list.
- After reaching the end of the list, the load balancer cycles back to the first server.
- Advantages
- Simplicity: Easy to implement and understand.
- Fair Distribution: Ensures that all servers receive an equal number of requests over time.
- Disadvantages
- Server State Unawareness: If a server is currently under high CPU load because it has triggered a program bug and entered a dead loop, the load balancing system is unaware of this and will continue to send requests to it.
- Unequal Load: Does not account for server capacity, potentially leading to imbalances if servers have different capabilities.
Weighted Round Robin
The Weighted Round Robin algorithm assigns a weight to each server based on its capacity or performance. Servers with higher weights receive more requests, ensuring that more powerful servers handle a larger share of the load.
Like the Round Robin method, it is not aware of a specific server running state.
- How It Works
- Each server is assigned a weight.
- The load balancer distributes requests to servers in proportion to their weights.
- Servers with higher weights are selected more frequently.
- Advantages
- Simplicity: Easy to implement and understand.
- Better Load Distribution: Accounts for server capacity, leading to a more balanced distribution of load.
- Customizable: Can adjust weights dynamically based on server performance and capacity.
- Disadvantages
- Server State Unawareness: If a server is currently under high CPU load because it has triggered a program bug and entered a dead loop, the load balancing system is unaware of this and will continue to send requests to it.
Lowest Load First
The load balancing system assigns tasks to the server with the lowest current load, where load can be measured by different metrics (including connection count, CPU load, I/O load, memory usage, etc.) depending on the type of task and business scenario.
This algorithm aims to distribute the workload evenly across all servers based on their current load.
- How It Works
- Monitor Load: Continuously monitor the load on each server.
- Compare Load: Compare the load across all servers to identify the one with the lowest load.
- Forward Request: Direct the incoming request to the server with the lowest load.
- Advantages
- Dynamic Load Distribution: Adjusts in real-time based on the actual load, ensuring balanced resource utilization.
- Efficiency: Helps prevent any single server from becoming a bottleneck.
- Disadvantages
- Overhead: Requires continuous monitoring and updating of server load metrics, adding overhead to the load balancer.
- Complexity: The lowest load first algorithm can be much more complex compared to Round Robin. If the algorithm is not well-designed, the algorithm itself may become a bottleneck in performance or cause many inexplicable problems. So the algorithm, while sounding great, actually has to consider a lot of problems for real application scenarios.
Highest Performance First
The Highest Performance First algorithm directs incoming requests to the server with the highest performance capabilities. Performance can be evaluated based on various metrics, such as processing power, response time, or throughput.
This algorithm aims to leverage the most powerful servers to handle the bulk of the workload.
- How It Works
- Evaluate Performance: Continuously evaluate the performance of each server.
- Compare Performance: Compare the performance metrics across all servers to identify the one with the highest performance.
- Forward Request: Direct the incoming request to the server with the highest performance.
- Advantages
- Optimal Resource Utilization: Ensures that the most capable servers handle the majority of the workload, maximizing efficiency.
- Improved Performance: Helps maintain fast response times by leveraging high-performance servers.
- Disadvantages
- Imbalance Risk: Can lead to imbalanced load distribution if high-performance servers consistently handle more requests, potentially overloading them.
- Complexity: The algorithm is also complex. Specific performance configurations need to be judged and selected based on the actual business. It’s also a complicated thing to do, and requires continuous tuning to achieve the optimal design even after the system is live.
Hash
The Hash algorithm distributes requests based on a hash function applied to a key, such as the client’s IP address or session ID. This ensures that requests from the same client are consistently directed to the same server.
- How It Works
- The load balancer applies a hash function to a key (e.g., IP address).
- The hash value determines the server to which the request is forwarded.
- Advantages
- Consistency: Ensures that requests from the same client are directed to the same server, which is useful for session persistence.
- Disadvantages
- Imbalance: May lead to uneven load distribution if the hash function does not distribute requests uniformly.
Reference:
- Li, Yunhua (2018) Learn Architecture from 0. Geek Time.
- https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/performance/what-is-load-balancing/