- What is the Cost of Planning?
- Project Cost Management
- Planning Processes and Outputs for Project Cost Management
- Possible Contents of a Cost Management Plan
- Estimating the Cost of Activities
- Cost Budgeting
What is the Cost of Planning?
- Once the project’s schedule has been created, we set out to determine the detailed budget for the project.
- Although the Project Charter provides the project budget, it is an approximate figure expected to have a certain percentage of variance.
- At this stage, we carry out a detailed estimation of all the project costs and determine whether this budget fits within the one mentioned in the project charter or not.
- If it does not fit, we either need to increase the budget mentioned in the project charter or reduce the scope.
Project Cost Management
- Project cost management includes the processes required to ensure that a project team completes a project within an approved budget
- The main planning tasks are planning cost management, estimating costs, and determining the budget
-
The main documents produced include a cost management plan, a cost estimate, and a cost performance baseline
- The purpose of this process is to determine the policies, procedures, and documentation for planning, managing, executing, and controlling project costs
- The project team holds meetings, consults with experts, and analyses data to help produce a cost management plan, which becomes a component of the project management plan
Planning Processes and Outputs for Project Cost Management
| Knowledge area | Planning process | Outputs |
|---|---|---|
| Project cost management | Plan cost management Estimating costs Determining the budget |
Cost management plan Cost estimate Cost performance baseline |
Possible Contents of a Cost Management Plan
- Units of measure, such as staff hours or days or a lump sum amount, currency to be used, inflation assumptions, etc.
- Level of precision for cost estimates, such as how to round numbers
- Level of accuracy, such as +/-10%
- Organizational procedure links
- Control thresholds for monitoring cost performance, such as a percentage deviation from the baseline plan
- Rules of performance measurement, especially if earned value management is used
- Reporting formats and frequency for cost reports
- Additional details about cost activities, such as strategic funding choices, procedures to account for currency fluctuations, and procedures for recording costs
Estimating the Cost of Activities
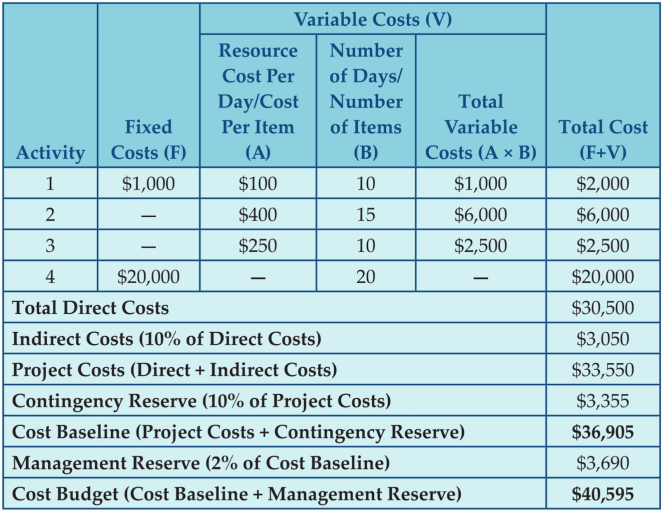
- The first step towards creating a project budget is by estimating the costs associated with each activity. There can be fixed and variable costs.
- If any equipment is bought for it or if any setup costs are involved, then these will be the fixed costs for the activity.
- Any use of materials or human resources would generally entail variable costs.
- All these costs are then added to get the total costs for the activity
- We generally estimate only the variable costs associated with the project activities.
Estimating Costs
- Project teams normally prepare cost estimates at various stages of a project, and these estimates should be fine-tuned as time progresses.
- It is also important to provide supporting details for the estimates, including ground rules and assumptions (sometimes called the basis of estimates)
- A large percentage of total project costs are often labour costs, so it is important to do a good job estimating labour hours and costs
Cost Estimating Techniques
- Analogous estimates, also called top-down estimates, use the actual cost of a previous, similar project as the basis for estimating the cost of the current project.
- This technique requires a good deal of expert judgments and is generally less costly than others are, but it can also be less accurate
- Bottom-up estimates involve estimating individual activities and summing them to get a project total.
- This approach can increase the accuracy of the cost estimate, but it can also be time intensive and, therefore, expensive to develop
- Parametric modelling uses project characteristics (parameters) in a mathematical model to estimate project costs
Cost Estimating Process
- See the detailed steps, ground rules, and assumptions that are used for developing the cost estimate in the following table
- Also, summary information was documented in a cost model under this table
- Just as projects are unique, so are cost estimates
- Consult with internal and external experts and organizations for assistance
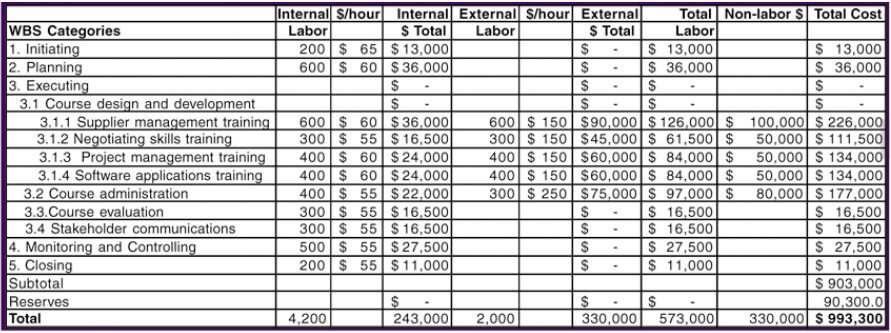
A Sample of Cost Estimate
Assumptions:
- Internal labor rates include benefits and overhead. Average hourly rates based on skill levels and departments.
- External labor rates are based on historical average; may change as contracts are awarded.
- Non-labor costs include purchasing licenses for using training materials, books, DVDs, travel expenses, etc.; may change as contracts are awarded.
- Reserves are calculated by taking 10% of the subtotal for the estimate. These contingency reserves are based on known risks.
Cost Budgeting
- Project cost budgeting involves allocating the project cost estimate to tasks over time
- The tasks are based on the work breakdown structure for the project
- The main goal of the cost budgeting process is to produce a cost baseline, or time phased budget, that project managers use to measure and monitor cost performance.
- Coming up with a project budget is a simple addition of all the individual activity estimates.
- However, there are also some additional items that need to be added to get the final budget.
- These are two levels of reserves - contingency reserve and management reserve.
Contingency and Management Reserve
- Contingency reserve is kept for known risks on the project.
- For example, if one of the risks on the project is related to thefts, then some amount will be kept aside to take care of the damage caused by this risk.
- Management reserve is for unknown risks.
- There are several things that the project manager may not envision within the project.
- If they do occur, some money needs to be kept aside to handle the damage. This amount is the management reserve.
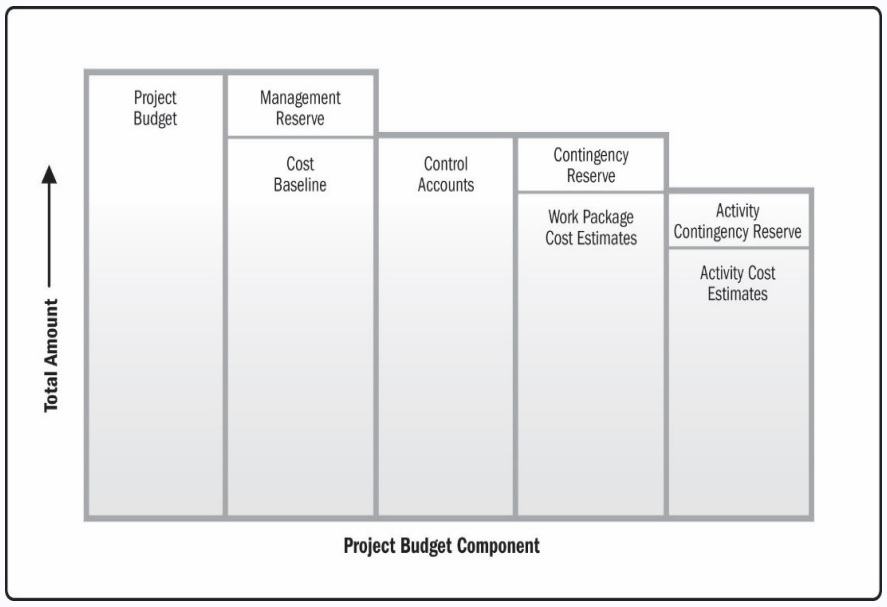
Project Budget Components
- Cost estimates from the various activities along with any contingency reserves associated with them create the work package cost estimates.
- The work package cost estimates plus any contingency reserves associated with them create the control accounts.
- The summation of all control accounts equals the cost baseline.
- Management reserve plus the cost baseline equals the project budget.