Project Risk Management
- PMI defines a project risk as an uncertainty that can have a negative or positive effect on meeting project objectives
- Risks may be negative ones that cause harm to the project (called threats) or positive ones that cause benefit to the project (called opportunities).
- We are most often worried about the threats as they have the ability to derail the project.
- Inadequate risk planning is the top cause of project failures.
- The main planning processes in risk management planning are:
- identifying risks
- analysing risks
- responding to risk.
Identifying Risks
- The first and the most important step in risk management planning is to identify all the project risks.
- You cannot manage risks until you identify them
- Identifying risks involves determining which risks are likely to affect a project and documenting the characteristics of each
- The main outputs of this process are a risk register and a risk report
- The most common ways of identifying risks on a project are brainstorming, historical information, and checklists.
What Is a Risk Register?
- A risk register is a document used as a risk management tool to identify potential setbacks within a project.
- The aims of risk register are to collectively identify, analyse, and solve risks before they become problems.
- While usually cantered around projects, other circumstances where risk management is helpful include product launches and manufacturing.
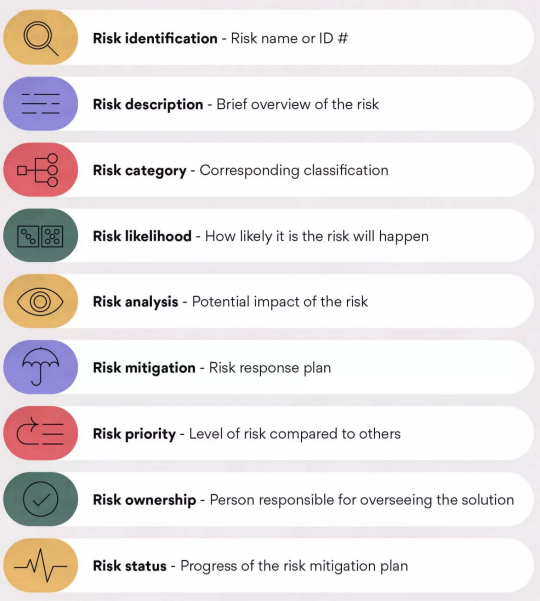 What included in a risk register
What included in a risk register
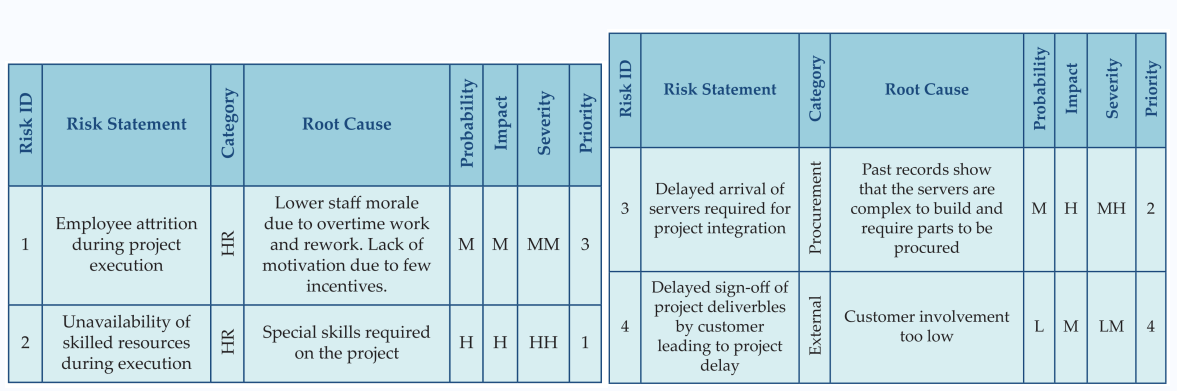
Analysing Risk
- Severity is just the combination of probability and impact
- Based on the combination, the priority is decided.
Responding to Risks
Once the risks have been prioritised, we need to do something about them, so they do not interfere with the project objectives. We start with the top priority risk and go down.
- The responses to risk could be: Avoid, Mitigate, Transfer, or Accept.
- Avoiding a risk means taking actions to completely remove the risk.
- The most common response to risks is mitigation.
- Mitigation means a reduction in the probability or impact of risk, or both.
- Transfer of risk takes place when our actions transfer the risk to a third party.
- The most common ways of transferring are outsourcing and insurance.
- Finally, if nothing can be done about a risk or a risk is too low in priority, we may decide to accept the consequences of the Risk.