Read-write separation disperses the pressure of database read-write operations, but does not disperse the storage pressure. When the amount of data reaches ten million or even hundreds of millions of data, the storage capacity of databases will become the bottleneck of the system, which is mainly reflected in these aspects:
- The performance of reading and writing will be degraded when the data volume is too large, and even with indexes, the indexes will become very large and the performance will be degraded as well.
- Data files can become very large, and database backup and recovery can take a long time.
- The larger the data files, the higher the risk of losing data in extreme cases.
So, we need the Database Sharding and Partitioning to solve these problems.
Database Sharding
Database sharding is a horizontal partitioning technique where a large database is divided into smaller, more manageable pieces called shards. Each shard is an independent database that contains a subset of the total data. Sharding helps distribute the data and workload across multiple servers, improving performance and scalability.
Key Features of Sharding
- Horizontal Partitioning: Data is split across multiple database instances based on a sharding key.
- Independent Databases: Each shard operates as a standalone database, which can be managed and scaled independently.
- Scalability: Sharding allows for horizontal scaling by adding more shards to distribute the load.
How Sharding Works
- Choose a Sharding Key: Select a key to determine how data will be distributed across shards. This key is typically a field in the data, such as a user ID or geographic location.
- Distribute Data: Use the sharding key to distribute data across multiple shards. Each shard contains data corresponding to a specific range or hash value of the sharding key.
- Route Queries: Implement a mechanism to route queries to the appropriate shard based on the sharding key.
For example:
Consider a social media application with millions of users. By sharding the user data based on user IDs, you can distribute the data across multiple shards. For example:
- Shard 1: Users with IDs 1-100,000
- Shard 2: Users with IDs 100,001-200,000
- Shard 3: Users with IDs 200,001-300,000
Challenge
- Join Operation
- Business databases often distribute tables that used to be in a single database across multiple databases. This can make it difficult to use SQL
Joinacross different databases.
- Business databases often distribute tables that used to be in a single database across multiple databases. This can make it difficult to use SQL
- Transaction
- After database sharding, the tables are distributed to different databases and cannot be modified in a transaction.
- While database vendors offer some solutions for distributed transactions (e.g., MySQL’s XA), the performance is too low and goes against the goal of high-performance storage.
- Cost
- Business databases also incur additional costs. What was originally handled by one server may now require multiple servers, increasing infrastructure expenses.
So, based on the above issues, database sharding is not recommended for start-up businesses. Because there is a lot of uncertainty in the start-up business. And there is no storage and access pressure when the business starts, database sharding is not valuable to the business.
For large companies, however, it’s a different story. Large companies usually already have a mature solution for database sharding. And even if it is an experimental new business, the scale of users is massive. Therefore, for large companies, it is best to consider the database sharding at the beginning of the design.
When designing the architecture, tend to choose simple and appropriate solutions (don’t choose the most advanced solution, which may not be suitable for your project).
Database Partitioning
Database partitioning is a technique used to divide a large database table into smaller, more manageable pieces called partitions. Unlike sharding, partitioning is typically done within a single database instance. Partitioning improves performance by enabling the database to handle smaller chunks of data and allows for more efficient query processing.
Key Features of Partitioning
- Vertical or Horizontal Partitioning: Data can be partitioned either vertically (by columns) or horizontally (by rows).
- Single Database Instance: Partitioning is usually performed within a single database instance.
- Performance Optimization: Partitioning enables more efficient query processing and management of large tables.
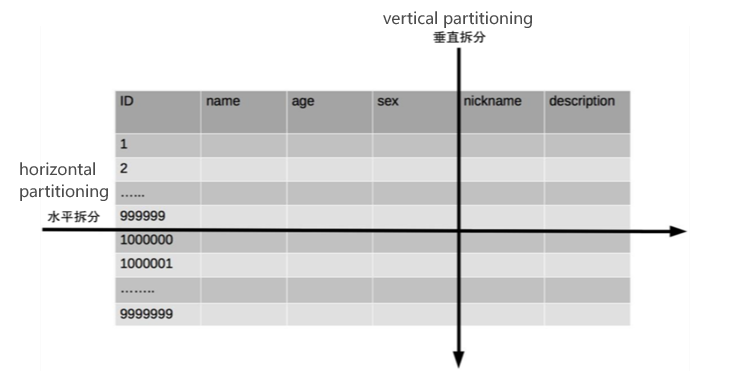 Vertical and Horizontal Partitioning
Vertical and Horizontal Partitioning
How Partitioning Works
- Choose a Partition Key: Select a key to determine how data will be partitioned. This key is typically a column in the table, such as a date or an ID.
- Define Partitions: Define the partitions based on the partition key. Each partition contains a subset of the data.
- Manage Partitions: Use database management tools to manage the partitions, including creating, merging, and deleting partitions.
For example:
Consider an e-commerce application with a large orders table. By partitioning the table based on the order date, you can divide the data into monthly partitions. For example:
- Partition 1: Orders from January 2022
- Partition 2: Orders from February 2022
- Partition 3: Orders from March 2022
Challenge
Vertical Partitioning
Vertical table splitting allows you to split out columns which are not commonly used and take up a lot of space in the table. For example, in a social media site, split the user’s nickname and description fields. This improves query performance for commonly used fields ( e.g., age and sex).
But it also increases operational complexity. Fields that could have been fetched in one query now require two queries.
Horizontal Partitioning
- Routing
- After horizontal partitioning, a routing algorithm is needed to calculate which sub-table a particular piece of data belongs to. This algorithm can sometimes be complex. Common routing algorithms include:
- Range Routing: Segmentation based on ordered columns of data (e.g., id numbers, timestamps). The advantage of range routing is that it is simple to expand new tables. The disadvantage is the possibility of uneven distribution.
- Hash Routing: Disperses based on the Hash value of a column. The advantage of hash routing is that the tables are more evenly distributed. The disadvantage is that it is not simple to expand the new table and all the data has to be redistributed.
- Configuration Routing: Independent table records routing information. Query the corresponding sub-table based on the table record. The advantage is that the design is simple and very flexible to use. The disadvantage is that it must be queried one more time, which can affect overall performance.
- After horizontal partitioning, a routing algorithm is needed to calculate which sub-table a particular piece of data belongs to. This algorithm can sometimes be complex. Common routing algorithms include:
- Join Operation
- Data is spread across multiple tables, and Join operations require multiple queries and merging of results.
- Count Operation
- The count operation becomes complicated after horizontal partitioning. Common ways to handle this:
count()Summing: Sums up thecount()operations of the sub-tables. This is simple to implement but low performance.- Record Count Table: Maintain a record count table, record the number of records in each sub-table, and update it when inserting and deleting. Good performance but high complexity.
- The count operation becomes complicated after horizontal partitioning. Common ways to handle this:
- Order by Operation
- Sorting needs to query the data of each sub-table separately and then merge and sort, which is a complicated operation.
Similar to the database read-write separation, the specific implementation of Database Sharding & Partitioning is also Code Encapsulation and Middleware Encapsulation. But the implementation will be more complex.
Reference:
- Li, Yunhua (2018) Learn Architecture from 0. Geek Time.
