Project Management Process Groups are a set of five interrelated and distinct phases (Initiating, Planning, Executing, Monitoring and Controlling, Closing) that cover the entire project management life cycle. They provide a framework for organizing and managing projects effectively.
- What Is a Systems Approach?
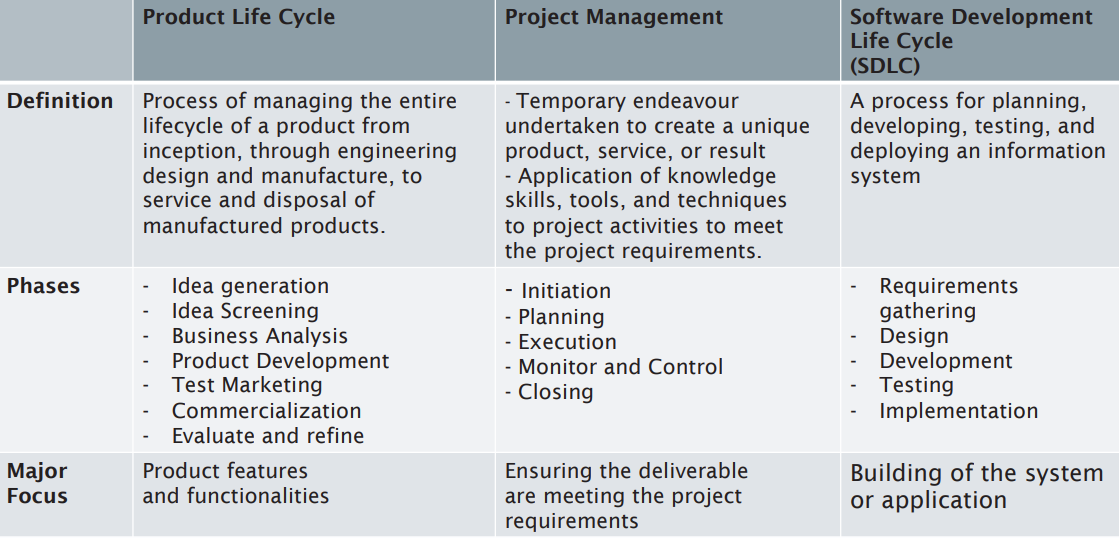
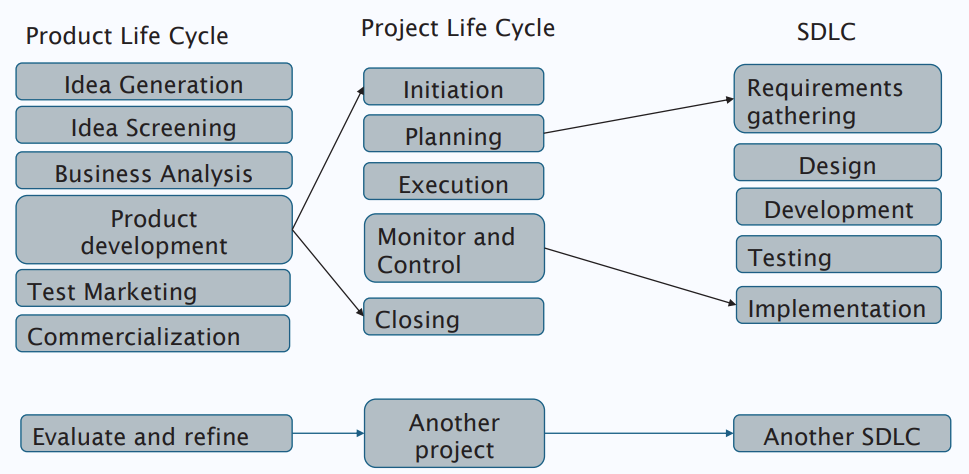
- Product Life Cycle / Project Life Cycle / SDLC
- Project Life Cycle Models
- Knowledge Areas and Process Groups in Project Management
- Characteristics of the Process Groups
- Related Blogs
What Is a Systems Approach?
-
A systems approach emerged in the 1950s to describe a holistic and analytical approach to management and problem-solving
-
Three parts include:
- Systems philosophy: an overall model for thinking about things as systems
- Systems analysis: problem-solving approach
- Systems management: address business, technological, and organisational issues before making changes to systems
Product Life Cycle / Project Life Cycle / SDLC
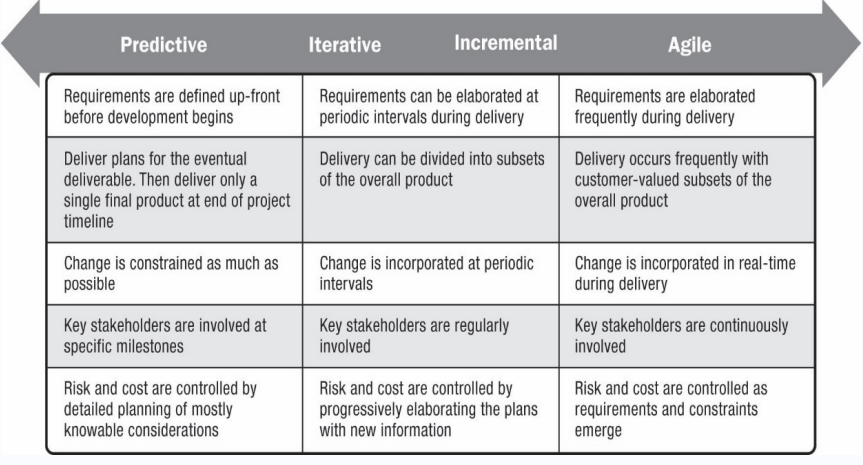
Project Life Cycle Models
- Predictive life cycle: The scope, schedule, and cost are determined early, and changes to scope are carefully managed.
- Project Management Institute (PMI) also refers to predictive life cycles as waterfall.
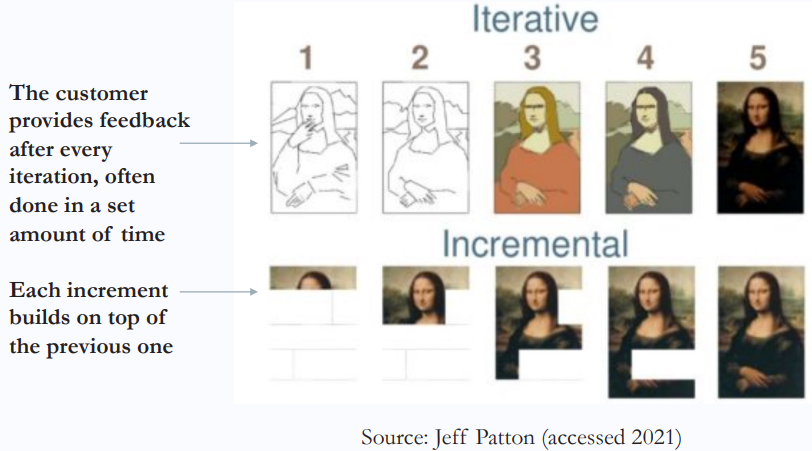
- Iterative life cycle: The scope is determined early, but time and cost estimates are modified as the understanding of the product increases.
- Iterations are used to develop the product through a series of repeated cycles to add to the functionality of the product.
- This approach works best when there is a high degree of change and a low frequency of delivery.
- Incremental life cycle: Deliverables are produced through a series of iterations that add functionality within a set time frame.
- The deliverable is not complete until after the final iteration.
- This approach works best when there is a low degree of change and a high frequency of delivery.
- Adaptive life cycle: Stakeholders define and approve the detailed scope before the start of an iteration, producing a usable product at the end of each iteration.
- PMI also refers to adaptive life cycles as agile or change-driven.
- This approach works best when there is a high degree of change and a high frequency of delivery.
- Hybrid life cycle: A combination of approaches is used based on the nature of the work.
- For example, some deliverables might have a low degree of change and low frequency of delivery such as monthly or quarterly progress reports.
- On the other had a high degree of change and a high frequency of delivery such as certain software features, and so on.
Predictive Life Cycle Models
- Waterfall model: has well-defined, linear stages of systems development and support
- Spiral model: shows that software is developed using an iterative or spiral approach rather than a linear approach
- Prototyping model: used for developing prototypes to clarify user requirements (heavy user involvement)
- Rapid Application Development (RAD) model: uses an approach in which developers work with an evolving prototype.
- This life cycle model also requires heavy user involvement and helps produce systems quickly without sacrificing quality.
Knowledge Areas and Process Groups in Project Management
- Project management consists of 10 knowledge areas:
- Integration, scope, schedule, cost, quality, resource, communications, risk, procurement, and stakeholder management
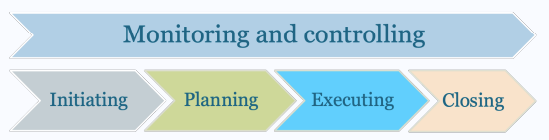
- Projects involve five project management process groups:
- Initiating, planning, executing, monitoring & controlling, and closing
Alpha (Excellent) PM spends more time on planning and pay off in execution:
| Process Group | Alpha PM | Average PM | Alpha Difference (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initiating | 2% | 1% | 100% more |
| Planning | 21% | 11% | 91% more |
| Executing | 69% | 82% | 16% less |
| Monitoring & Controlling | 5% | 4% | 25% more |
| Closing | 3% | 2% | 50% more |
| Total | 100% | 100% |
Characteristics of the Process Groups
- The amount of resources and length of each process group varies for every project
- Normally, executing tasks requires the most resources and time, followed by planning tasks
- Monitoring and controlling processes are done throughout the project’s life span
- Initiating and closing tasks are usually the shortest (at the beginning and end of a project or phase, respectively), and they require the least amount of resources and time
- However, every project is unique, so there can be exceptions
Related Blogs
- Initiating Projects (Process Groups)
- Planning Projects - Scope (Process Groups)
- Planning Projects - Schedule (Process Groups)
- Planning Projects - Cost (Process Groups)
- Planning Projects - Quality (Process Groups)
- Planning Projects - Resource (Process Groups)
- Planning Projects - Communication (Process Groups)
- Planning Projects - Risk (Process Groups)